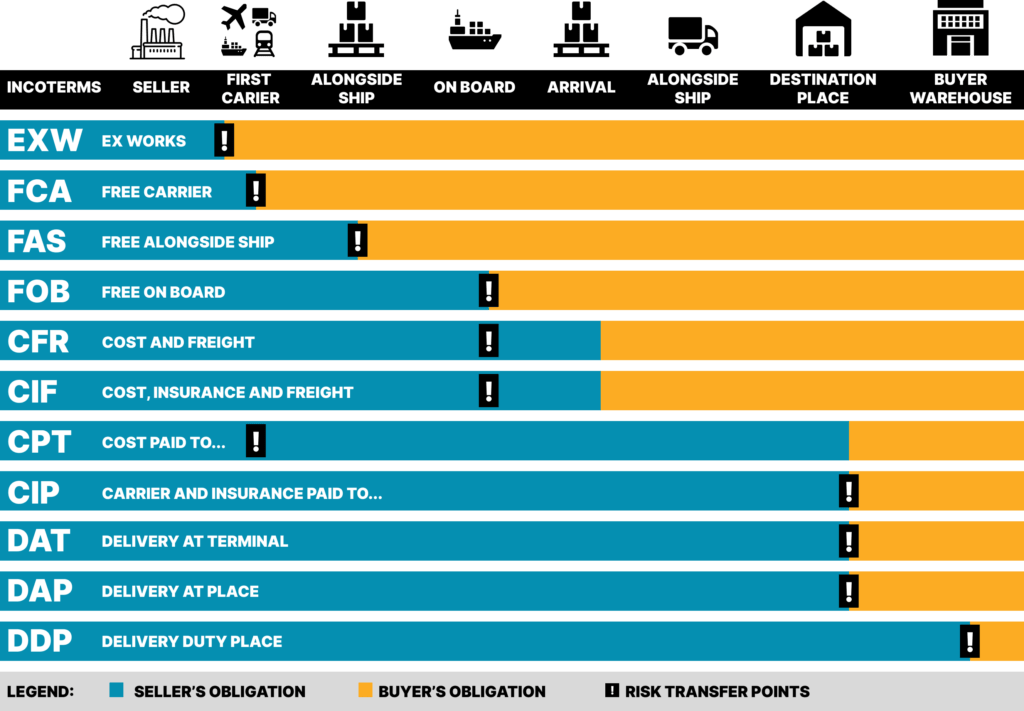
EXW imposes only minimal obligations on the seller, requiring him to deliver the goods to the buyer at the specified place of delivery and within the agreed time specified in the contract. The seller bears all risks of loss or damage until the goods are delivered, while any costs are borne by the buyer.
The FCA requires the goods to be delivered when they arrive at the specified place, are ready for unloading and are placed at the disposal of the carrier designated by the buyer.
Since FAS transfers the risk/loss to the buyer and requires the seller to clear the goods for export, it is more suitable for situations where the goods will only be delivered to the carrier before being placed alongside the vessel.
FOB transfers the risk of loss/damage to the buyer once the goods are placed on board and the seller has no obligation to enter into a contract of carriage.
The seller is obliged to contract for the transportation of the goods to the port of destination, to bear all costs associated with unloading and to clear the goods for export and not for import.
CIF is similar to CFR, but requires the seller to enter into a contract of carriage to the port of destination, bear all costs and clear the goods through customs for export, not import.
The CPT requires the seller to enter into a contract for the transportation of the goods from the point of delivery to the destination, but does not require the seller to enter into an insurance contract.
Seller and buyer, CIP and CPT have the same obligations and in addition, there is an obligation to contract insurance to cover the buyer's risk/damage to the goods from delivery to destination.
DAT (Delivery at Terminal) is one of the terms defined in the International Trade Terms (Incoterms) developed by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC). It refers to a transportation contract where the seller is responsible for delivering the goods to a specific terminal at the port of destination.
The DDP requires the seller to complete the transportation contract or arrange transportation at its own expense, but no insurance contract is required.
DAP is used when the place of delivery and destination are the same and the parties do not want the seller to bear the risks and costs of unloading. The seller is not obliged to unload the goods from the transport vehicle at the destination, and neither the seller nor the buyer is obliged to sign an insurance contract.

We offer permanent and strong solutions by being respectful to the environmentally conscious society.
sales@kitalogistics.com
germany@kitalogistics.com
almadm@kitalogistics.com
tasadm@kitalogistics.com
| Cookie name | Active |
|---|